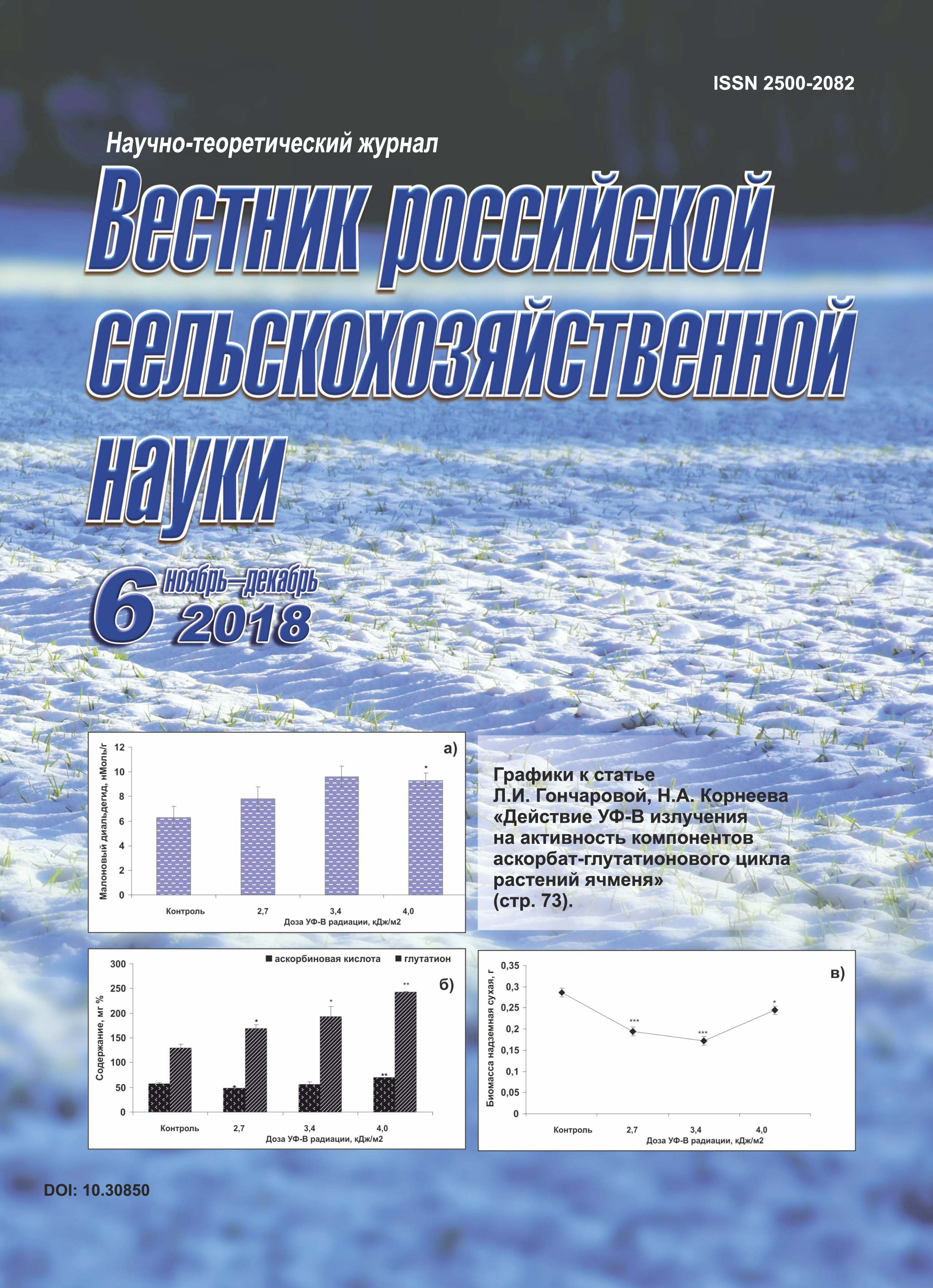
APPLICATION OF WATER WITH INCREASED CONCENTRATION OF SALTS FOR IRRIGATION
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.30850/vrsn/2018/6/84-86Keywords:
irrigation, low-mineralized water, salt content, drop irrigation, leaching operations, membrane technologyAbstract
The possibility of irrigation with low-mineralized water, the peculiarities of salt accumulation in the soil under drip irrigation, and the use of this method to remove accumulated salts from the root zone of the soil are considered. Technologies to reduce negative effect of salt content in irrigation water, including those protected by patents of the Russian Federation are presented. Irrigation of weakly-mineralized water containing up to 3 g/ l salts is possible under certain restrictions it specific processing in installations, which reduce total salt content and provide balance in ionic composition, which eliminates salinization and the development of soil alkalinity. Without special preparation water with a salinity more than 0.7 g / l can be used only against the background of high natural drainage of the site or artificial drainage with percolative moisture regime. More effective method of mineralized water preparation to irrigation is membrane technology application for selective deionization more dangerous for plants.